Introduction
Cloud computing elasticity is the capability of cloud platforms to modify computing resources in a real-time, automatic manner based on demand. It provides optimum infrastructure utilization, allowing businesses to automatically scale their resources up or down. Elasticity is an important aspect of cloud optimization to keep the cloud cost-effective, enhance performance, enforce security, and ensure compliance. CloudOpty offers a fine addition to this elasticity with the help of CloudScore™, a benchmarking tool that measures cloud optimization across industries.
Elasticity in cloud computing is when an information system is developed automatically to scale up or down depending on the incoming load. This provides an opportunity for the application or service to function optimally, without over-provisioning or under-provisioning.

Elasticity vs. Scalability
Though often used interchangeably, elasticity and scalability typically evoke very different meanings:
- Elasticity: Elasticity refers to the capacity of a cloud system to dynamically and automatically adjust its resources in real-time depending on the demands placed on the workload.
- Scalability: Scalability means growth, and it is usually met by adding more resources in order to satisfy some specific objectives of demand.
While scalability is generally considered to be a rather high-level term, elasticity refers predominantly to the application that automatically adjusts resources as a function of changing demand.
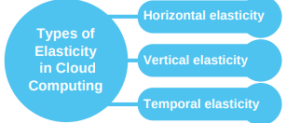
Types of Elasticity in Cloud Computing
Elasticity may be classified according to the nature of resourceallocation:
- Horizontal elasticity (scaling out/in): adding or removing instances of resources (e.g., virtual machines) to meet demand.
- Vertical elasticity (scaling up/down): increasing or decreasing the power of existing resources, such as upgrading CPU, memory, or storage.
- Temporal elasticity: Allows allocation of resources for a given period of time based on expected workloads.
The Mechanisms Behind Cloud Elasticity
Elasticity is attained by way of various key mechanisms:
1.Auto-Scaling: Auto-scaling monitors defined metrics and scales the number of active instances based on these metrics, all with little or nohuman intervention.
There are two types of auto-scaling:
- Reactive: a scaling technique based on the real-time feedback of the number of requests, CPU load, and memory consumption.
- Predictive: based on historical data, typically using machine learning models to trigger scaling before an increase in demand occurs.
2.Load Balancing: Load balancing is the distribution of incoming traffic among multiple servers to achieve even workload distribution, ensuring that bottlenecks are eliminated, enhancing reliability.
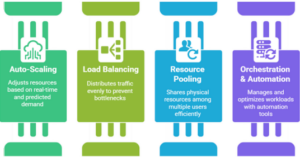
3.Resource Pooling: Cloud providers utilize multi-tenant architectures from which resources are pooled and dynamically allocated to users as needed, thereby ensuring maximum infrastructure utilization.
4.Orchestration and Automation: Automation and orchestration tools, including Kubernetes, Terraform, AWS Auto Scaling, and CloudOpty, make it much easier to manage workloads and optimize performance.
CloudOpty pivots on four core pillars of cloud optimization: Cost Optimization, Performance Booster, Compliance Canter, and Security Canter . Such pillars assure seamless cloud operations with maximized efficiency.

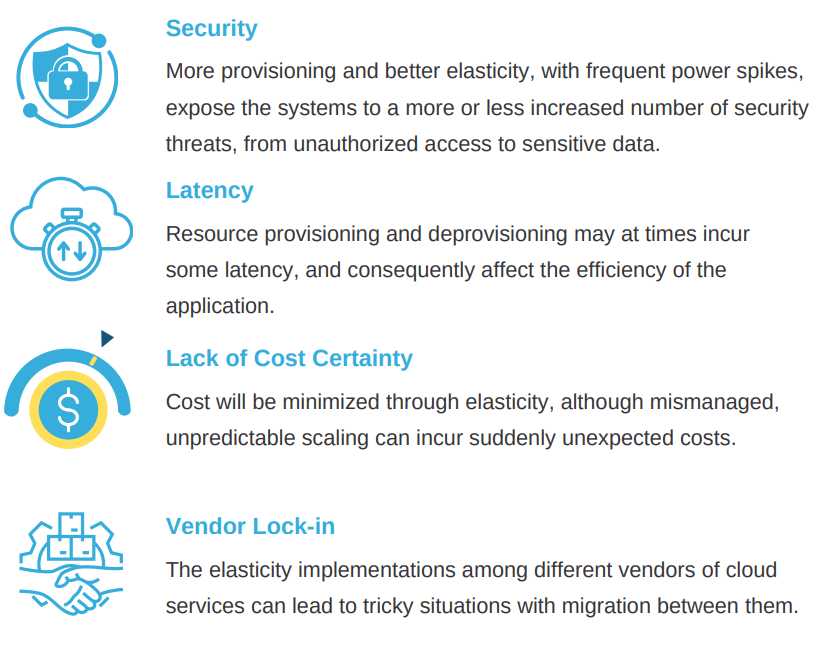
Challenges Related to Cloud Elasticity
Elasticity still comes on with outages, which raises several challenges:

Elasticity Use Cases in Cloud Computing
Elasticity operates as a single strength for countless applications in many industries:




Conclusion
Cloud elasticity is a critical feature of modern cloud computing. It offers organizations options to boost performance, increase cost efficiency, and enhance security. Yet modern computing needs to be monitored and optimized adequately for proper cloud elasticity management, thereby offering organizations a proper solution for cloud efficiency.
CloudOpty’s CloudScore™ and four-pillar approach enable organizations to benchmark efficiency in their cloud environments in order to reduce costs, enhance security, and ensure compliance for a fully optimized cloud environment.
In this light, greater investments are necessary for obtaining a powerful range of cloud optimization solutions in order to achieve cloud elasticity.
.
